FerriScan
MRI Measurement Of Liver Iron Concentration
FerriScan is internationally recognised as the gold standard in liver iron concentration (LIC) measurement and is included in a number of international Standards of Care.
FerriScan is a system for quantifying liver iron concentration (LIC) from specially acquired MRI images. The images used are standardised R2-MRI images (acquired using the ‘FerriScan protocol’) and proprietary internationally regulatory-cleared software is used to quantify liver iron concentration (LIC). Analysis is performed under stringent, quality controlled conditions (ISO 13485:2016 certified) in a central core laboratory by a team of highly trained engineers and physicists. FerriScan analysis has the highest sensitivity and specificity over the range of liver iron concentrations of any MRI-based method of LIC measurement, producing results that are reliable and reproducible over time and across different makes and models of MRI scanner. To date, FerriScan has been used to non-invasively measure LICs in over 50,000 patients.
FerriScan has international regulatory clearances. It was granted clearance by the FDA (US) for the quantification of LIC in 2005. In January 2013 FerriScan gained an additional clearance from the FDA as a companion diagnostic to aid in the identification and monitoring of non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia patients receiving therapy with deferasirox. FerriScan also has clearances form the TGA (Australia) and CE Mark (Europe).
The FerriScan process uses patented R2-MRI imaging technology. Once MRI images have been acquired, these images are securely transmitted via webportal to Resonance Health. The Resonance Health weportals are HIPAA, GDPR, and Privacy Act compliant. Once analysis is complete, results are returned via webportal. For information on data transfer processes and security please contact [email protected].
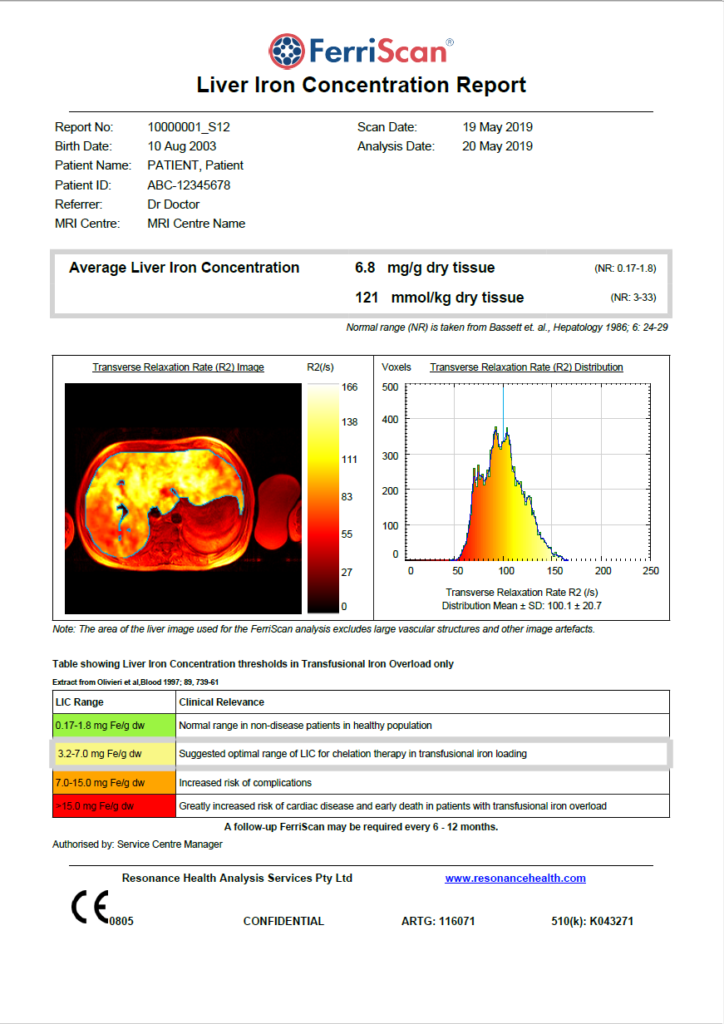
The FerriScan Report
FerriScan was originally calibrated against liver biopsy in patients with various iron overload conditions.
- The FerriScan technique is robust
- There is no shift in accuracy or precision across different MRI scanners
- FerriScan is unaffected by fibrosis or chelation therapy
- FerriScan can be used for patients of all ages including neonates
An increasing number of patient treatment guidelines for thalassaemia, sickle cell disease, myelodysplastic syndrome and haemochromatosis recommend using FerriScan to quantitatively measure liver iron concentration.
For a compiled list of treatment guidelines involving R2 MRI (FerriScan), please click here.
Key FerriScan Features
- FerriScan provides an accurate, validated MRI-based measurement of liver iron concentration
- FerriScan has high sensitivity and specificity for measuring LIC
- FerriScan is non-invasive, requires no contrast agents and has a scan time of approximately 7-9 minutes
- FerriScan measures across the full range of iron loading seen in clinical practice
- Image analysis and LIC reporting is performed at a central ISO 13485 certified core laboratory
- FerriScan has international regulatory clearances (FDA, CE Mark, TGA)
- Results are available within a target time of two business days
- FerriScan results are clinically validated to be unaffected by inflammation, fibrosis or cirrhosis
- FerriScan requires no breath-hold and may therefore be used for paediatric patients
- Results are accurate, reliable and reproducible over time and between MRI centres and all major makes and models of scanner (GE, Siemens, Philips)
- There is no requirement for customers to purchase new software or hardware
- FerriScan is suitable for 1.5 Tesla MRI scanners
- FerriScan is charged on a per analysis basis - no expensive upfront licence costs
Why Use FerriScan R2-MRI to Measure Liver Iron Concentration?
FerriScan is quick, easy and painless, with an MRI scan time of approximately 7-9 minutes. FerriScan is a free-breathing technique (no breath-hold required), and FerriScan does not require any contrast agents.
FerriScan provides a more accurate and reliable measure of LIC at any point in time than that provided by serum ferritin and patients need no longer undergo the painful, time consuming process of liver biopsy.
Unlike liver biopsy, which provides an analysis of LIC in only one small area, FerriScan analyses a cross-section of the liver. This area is typically thousands of times larger than biopsy, hence significantly reducing the biopsy sampling error.
The Liver iron Concentration (LIC) measurement can be used by clinicians to monitor iron loading and adjust treatment regimens accordingly.
FerriScan is being used by clinicians in over 45 countries worldwide to aid their diagnosis, management and monitoring of iron overload.
FerriScan is a solution with proven value in improving the health outcomes of patients suffering from diseases such as thalassaemia, sickle cell disease, haemochromatosis and myelodysplastic syndrome.
Advantages of FerriScan over serum ferritin (SF)
- Other factors present in patients with iron overload such as infection, inflammation, fever, cancer, metabolic disease, or liver damage may result in significant elevation of serum ferritin concentrations in the absence of iron overload;
- SF has poor accuracy for measuring body iron loading in patients with thalassaemia major;
- SF levels in patients with thalassaemia intermedia are significantly lower than in patients with thalassaemia major despite them having comparable Liver Iron Concentration (LIC) levels (as determined by biopsy), suggesting that SF significantly underestimates iron loading in patients with thalassaemia Intermedia;
- Increased serum ferritin concentrations may indicate iron overload, but are not a quantitative measure of iron burden. Additionally, once SF becomes saturated, there is poor correlation between SF and iron levels;
- SF is an imprecise and potentially misleading parameter on which to base clinical management decision in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD);
- The relationship between total body iron stores and SF in patients with hereditary haemochromatosis is very weak;
- SF has significant limitations in assessment of iron burden in children with SCD, and liver iron assessment therefore is necessary for optimal management.
Advantages of FerriScan over liver biopsy
- Non-invasive, painless, no risk of bleeding or infection;
- Provides information about the distribution of iron in the liver;
- The size of the biopsy specimen only represents 1/50,000th of the total mass of the liver, therefore the sampling error is potentially large - the location where the biopsy is taken from will affect the result, and may not be representative of the entire liver;
- FerriScan® measures iron in a volume of liver that is thousands of times greater than liver biopsy and therefore has a much smaller sampling error.
Advantages of FerriScan over Liver T2* (MRI)
- There are a number of liver T2* techniques and these are not standardised. Non standardisation means that it is very difficult to compare results. See Graph below;
- The liver T2* techniques are not regulatory cleared;
- As a patient’s LIC starts to climb, the liver T2* techniques become more unreliable and eventually fail at higher iron levels. This can occur from 15 mg/g dry weight (depending on method of acquisition and analysis);
- The liver T2* methods do not report across the full range of iron loading seen in clinical practice. (Published liver T2* methods measured LICs up to 23.6, 27.67 and 32.98 mg/g dry tissue, respectively.);
- The liver T2* techniques can be influenced by the presence of liver fat and fibrosis;
- A review of the literature shows that, unlike FerriScan® R2-MRI, liver T2* methods generate data that are scanner and method dependent and hence are not sufficiently standardised to enable reliable liver iron concentration measurements using calibration curves published from other centres;
- Liver T2* to LIC conversion is dependent on a number of factors including various scanning profiles, various methods of analysis, and which calibration curve is used. The variance in several T2* techniques can be seen in the tables below. For the purposes of comparison, the LIC result derived from a calculated liver T2* value of 2.5ms will vary widely depending on which calibration curve has been used for conversion.
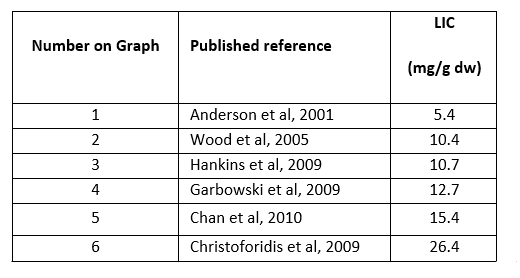
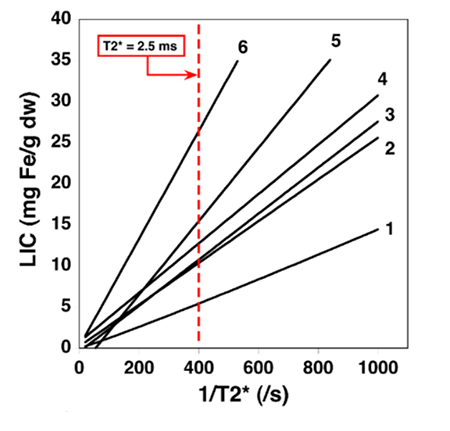
Graph shows various Liver T2* conversions to LIC.
FerriScan Resources
Click the link(s) below to access our resources. Need something else? Please contact our team at [email protected] for further information.
- FerriScan Fact Sheet
- FerriScan Fact Sheet - Sickle Cell Disease
- FerriScan Fact Sheet - Haemochromatosis
- FerriScan: Patient Management Guidelines
- FerriScan Scientific Publication
- FerriScan Case Study Booklet
- MRI Scanner Details Form (Register for Service)
- Evidence for the Effect of FerriScan Measurements on Outcome for Patients at Risk of Iron Overload from Blood Transfusions